U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks
The U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks are becoming focal points for investors and economists as signs of slowing growth and inflation shifts surface. Recent updates indicate a higher likelihood of an economic downturn in the U.S. and globally. J.P. Morgan Research has raised the probability of a recession beginning by the end of 2024 to 35%, up from its previous estimate, due to weakening labor data and slowing growth across various sectors.
Key Trends in U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks
In mid-2024, U.S. economic indicators showed resilience, but recent data paints a different picture. The labor market, once robust, is now showing signs of cooling. The July jobs report revealed a slight uptick in unemployment, marking four consecutive months of increases. Such trends suggest the U.S. economy is facing increased risks of a recession, with potential impacts on sectors ranging from technology to real estate.
1. Likelihood of a Recession
Given softer labor market data and other economic indicators, the probability of a recession has grown. J.P. Morgan Research recently adjusted its outlook, now estimating a 35% chance of a recession by 2024. This shift reflects growing vulnerabilities in the economic structure, including profit margin pressures, credit market stress, and geopolitical uncertainties. Looking beyond 2024, the chance of a recession by 2025 remains at 45%, emphasizing that recession risks will likely persist.
2. Interest Rate Trends
The U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks are also heavily tied to interest rate forecasts. As inflation shows signs of stabilizing, J.P. Morgan has reduced its outlook on prolonged high-interest rates. Now, there is only a 30% chance that the Federal Reserve will continue its current rate levels for an extended period, down from 50% previously. This change signals that the Fed may begin to lower rates if inflation further cools, allowing the economy to regain some momentum.

What Slowing Inflation Means for Recession Risks
Inflation trends have a significant role in shaping the U.S. economic outlook. As inflation decreases, there is less pressure on the Fed to maintain restrictive policies. Wage inflation has eased, and overall labor costs are closer to the Fed’s target. This change suggests that the Fed could adjust its policies and potentially lower interest rates, providing some relief to businesses and consumers.
In addition, cooling inflation means less strain on consumer purchasing power. However, the U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks remain uncertain, as inflationary pressures could still fluctuate based on global supply chains and geopolitical factors.

Labor Market and Economic Activity
The labor market’s cooling trend has been a central factor in raising concerns over the U.S. economic outlook and recession risks. Job growth is slowing, and some sectors are beginning to report layoffs. The service sector continues to expand, but manufacturing data shows contraction, which could be an early signal of a broader economic slowdown.
The weakened demand for labor aligns with broader recession risks, indicating potential future cuts in spending by consumers and businesses. Such spending reductions could push the economy into a recession. As such, investors and analysts closely monitor the latest labor reports to anticipate potential shifts in the U.S. economic outlook.
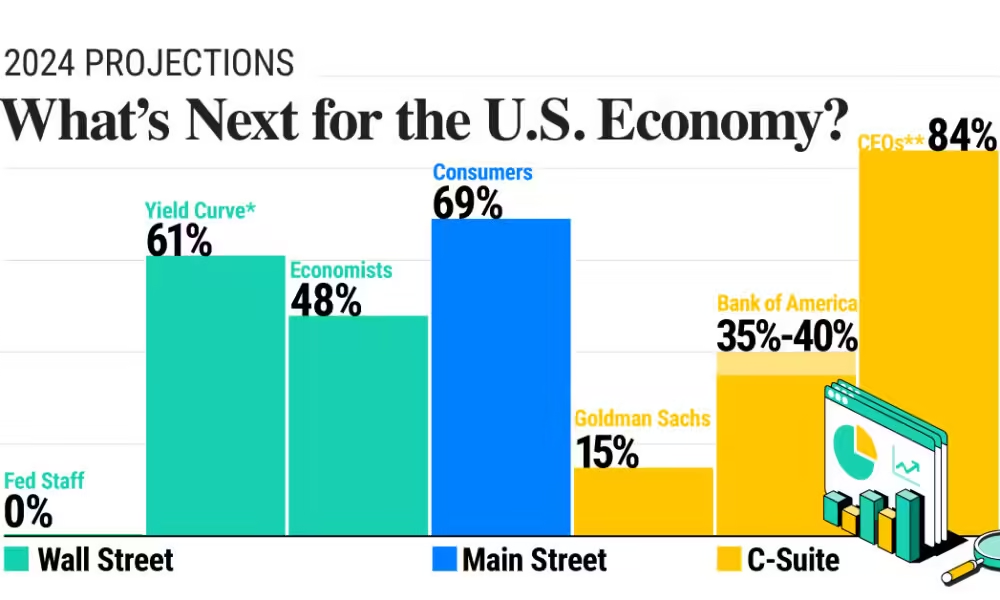
Comparing U.S. and Global Interest Rates
The U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks are not only tied to domestic trends but also global financial conditions. While the Fed may lower interest rates, other central banks worldwide might maintain their rate levels if inflation continues to vary significantly between regions. Historically, U.S. rate adjustments have limited effects on other economies unless synchronized by global economic fundamentals. Hence, if the Fed reduces rates, it may not necessarily mean similar rate cuts in other regions, adding complexity to global market reactions.
Summary of the U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks
The U.S. economy faces notable challenges as it contends with a higher probability of recession, potentially declining interest rates, and mixed signals in the labor market. These factors collectively shape a more cautious U.S. economic outlook for 2024 and beyond. As inflation moderates, the Fed may adopt a less aggressive rate policy, potentially mitigating some recession risks.
In conclusion, the U.S. Economic Outlook and Recession Risks depend on several moving pieces, including labor trends, inflation rates, and global financial conditions. These indicators suggest that investors should prepare for possible shifts in the economic landscape, as signs of a slowdown grow more apparent across multiple sectors.
Also read the other articles:
Shopify stock price prediction 2030
